  | |
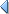
You can use the equality (==) operator to determine whether the values or identities of two operands are equal. This comparison returns a Boolean (true or false) value. If the operands are strings, numbers, or Boolean values, they are compared by value. If the operands are objects or arrays, they are compared by reference.
It is a common mistake to use the assignment operator to check for equality. For example, the following code compares x to 2:
if (x == 2)
In that same example, the expression x = 2 is incorrect because it doesn't compare the operands, it assigns the value of 2 to the variable x.
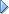
The strict equality (===) operator is like the equality operator, with one important difference: the strict equality operator does not perform type conversion. If the two operands are of different types, the strict equality operator returns false. The strict inequality (!==) operator returns the inversion of the strict equality operator.
The following table lists the ActionScript equality operators:
|
Operator |
Operation performed |
|---|---|
|
Equality |
|
Strict equality |
|
Inequality |
|
Strict inequality |
  | |